Tests in Android Development
App has 2 test types:
- Local unit tests - tests which can run on the JVM.
- Instrumented unit tests - tests which require the Android system.
Tests can be seperated to three main branches.
- Unit Tests
- Integrations Tests
- End to End Tests
Our testing strategy should include each of these types.
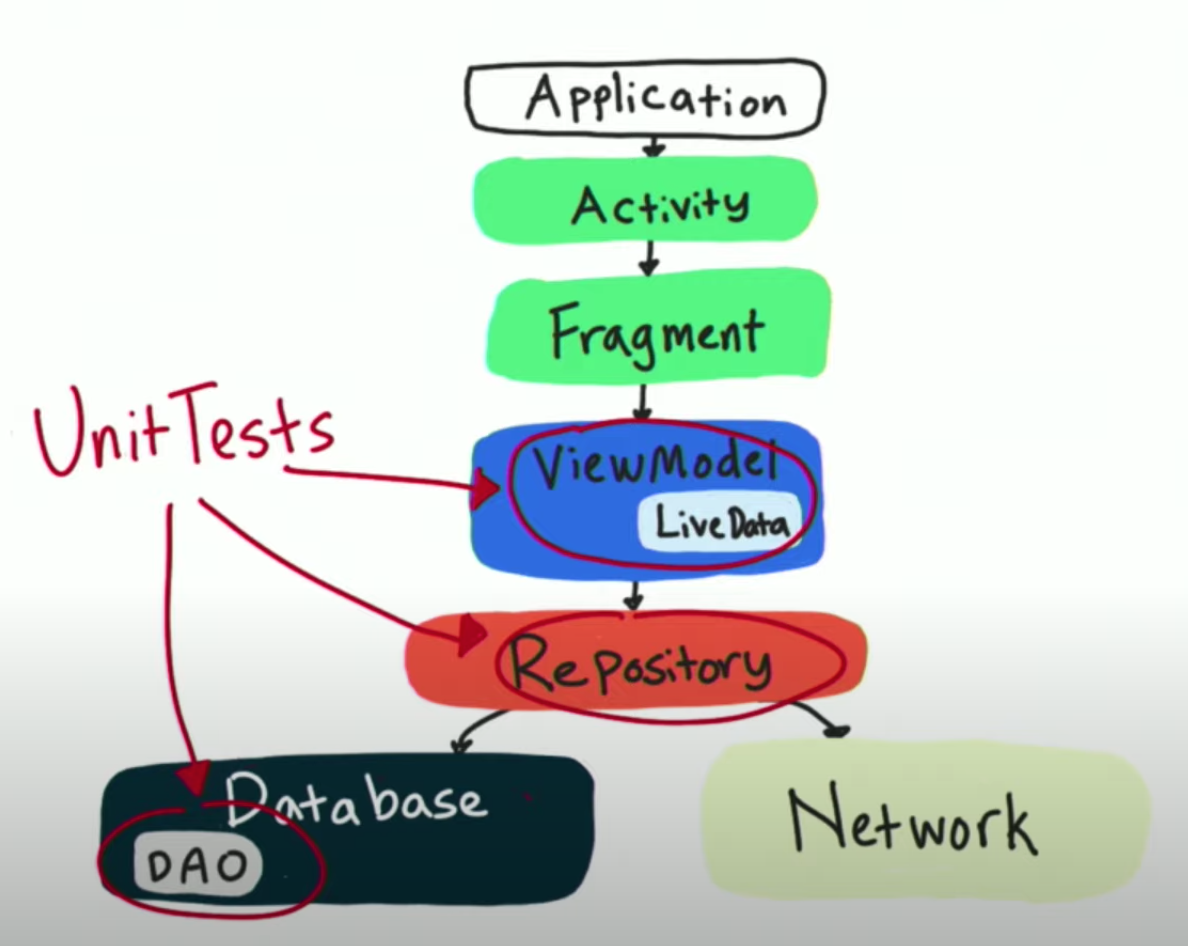
Unit Tests
- Unit tests scope of single method or class.
- When test fails we know exactly where the error is.
- Unit tests meant to run fast. Because they also meant to be run often.
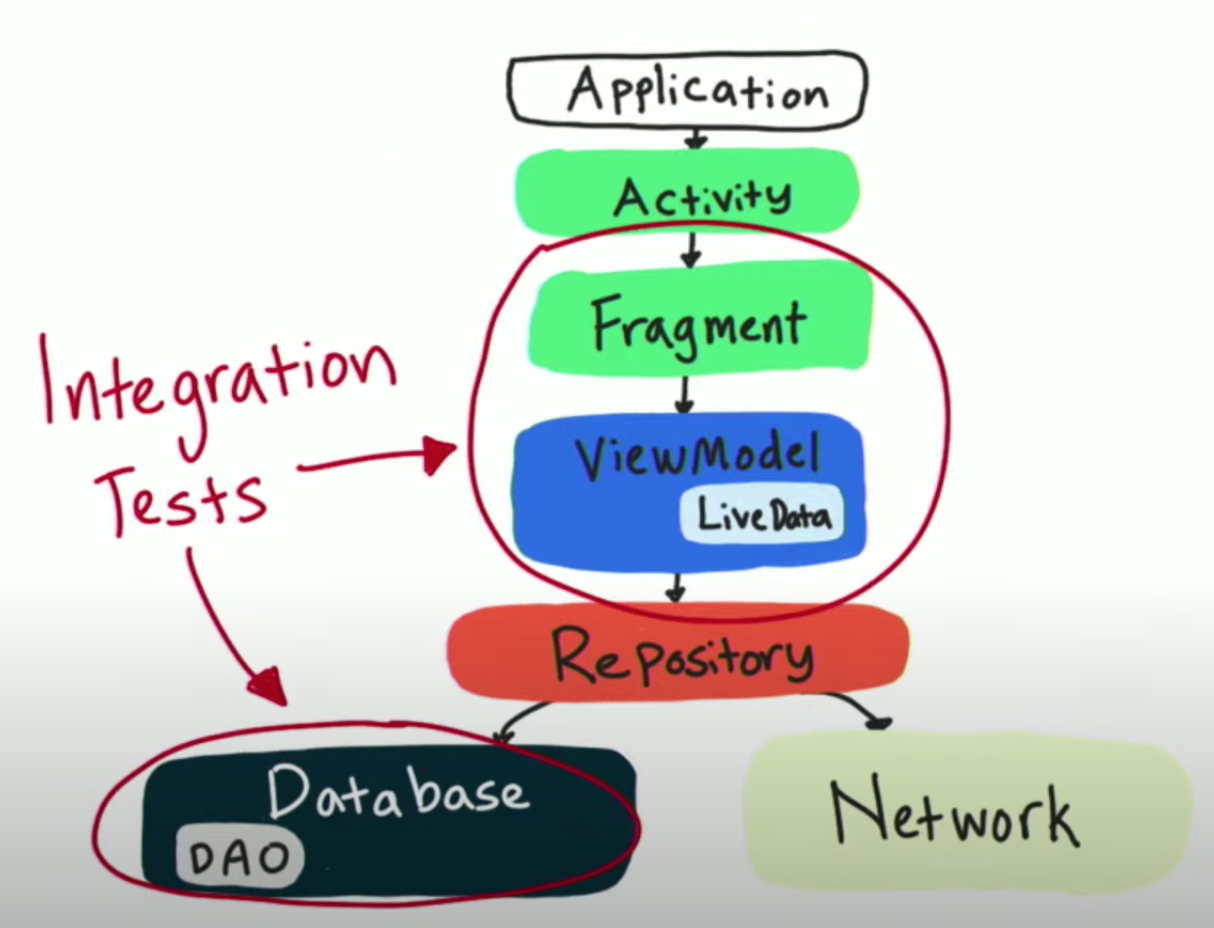
Integration Tests
- Several classes or a single feature
- Ensure classes work together successfully
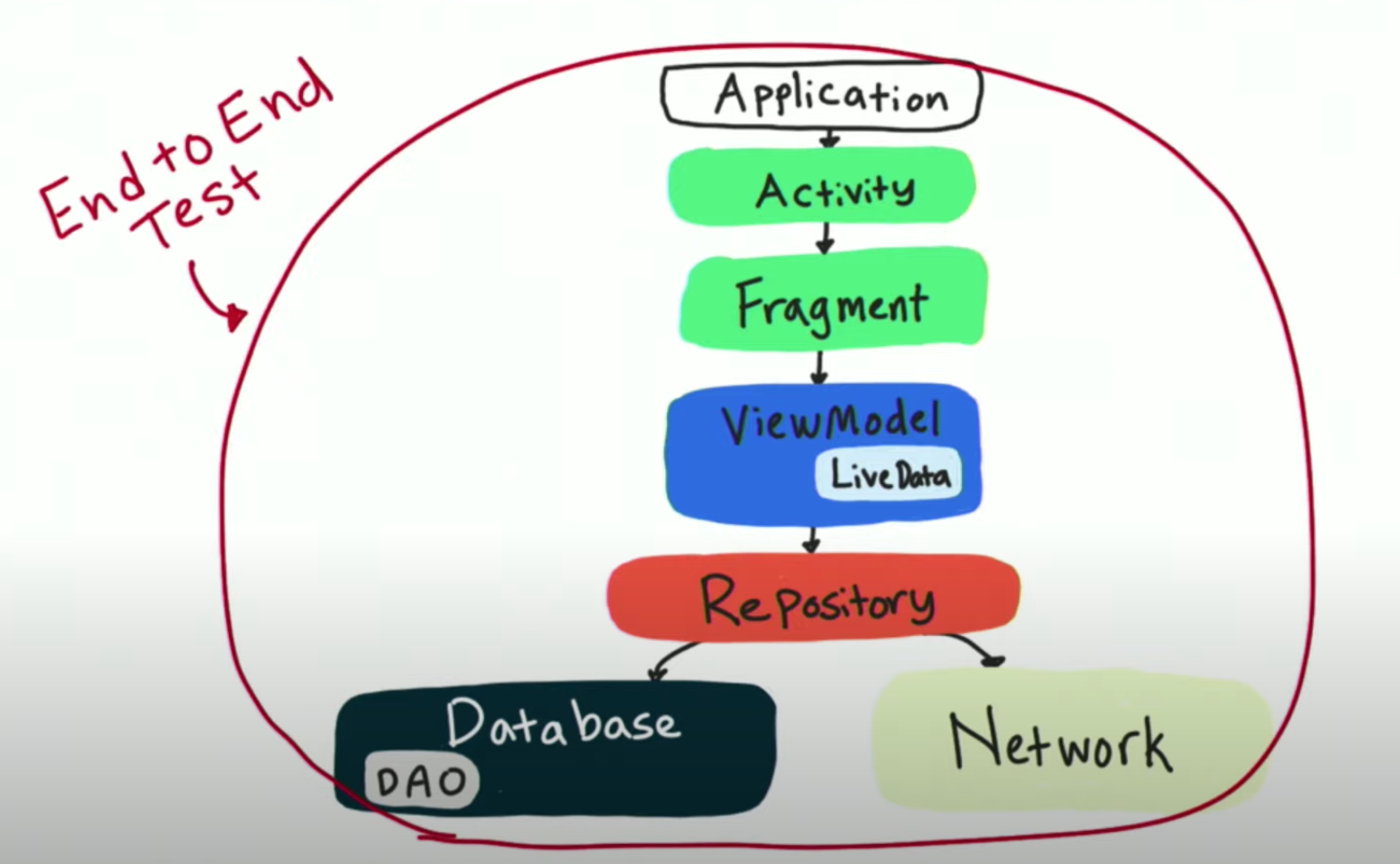
End-to-End Tests
- Combination of features working together
- Test the app work as a whole
- Simulate real usage, almost always instrumented
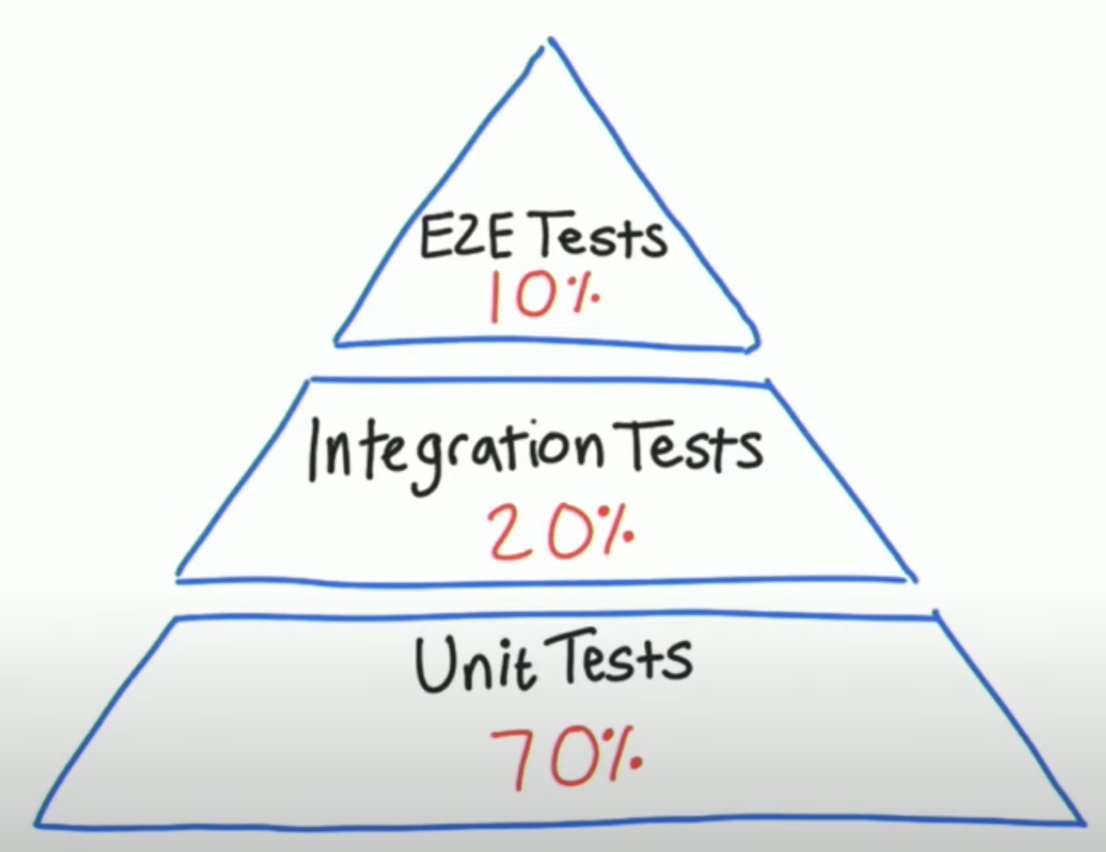
General Test Code Percentage
Test ViewModel
ViewModel unit test’leri local testler olmalı (Viewmodel sınıfı içinde android dependency’leri barındırmamalı). ViewModel içindeki bir modeli test etmek gerektiğinde view’dan bağımsız bir ViewModel instance‘ı oluştururuz.
val tasksViewModel = TasksViewModel()
Ama burda viewmodelimiz constructor’u içinde application objesine ihtiyaç duyuyor. Local test altında olduğumuz için uygulama ayağa kalkmadan test’ler çalışıyor ve elimizde bir application objesi yok. Bu gibi durumlarda AndroidX test kütüphalerini kullanabiliriz.
build.gradle/app altına aşağıdaki kütüphaneleri ekliyozuz.
testImplementation "androidx.test:core-ktx:$androidXTestCoreVersion"
testImplementation "org.robolectric:robolectric:$robolectricVersion"
testImplementation "androidx.test.ext:junit-ktx:$androidXTestExtKotlinRunnerVersion"
Ardından viewmodel’i oluştururken bir application objesi yaratabiliyoruz.
val tasksViewModel = TasksViewModel(ApplicationProvider.getApplicationContext())
Son olarak da bu hali ile test’in çalışabilmesi için Test sınıfının üstüne @RunWith(AndroidJUnit4::class)
annotation’ını eklememiz gerekiyor.
Test LiveData
LiveData testi yapabilmek için ilk olarak InstantTaskExecutorRule() sınıfına ihtiyaç vardır.
build.gradle/app altına aşağıdaki kütüpheyi eklememiz gerekiyor.
testImplementation "androidx.arch.core:core-testing:$archTestingVersion"
Test sınıfında test metodundan ayrı olarak aşağıdaki tanımı yapmak gerekiyor. Bu sayede
test metodu çağırılmadan önce livedata test’i için gerekli olan InstantTaskExecutorRule
sınıfı oluşturulmuş oluyor.
@get:Rule
var instantTestExecutorRule = InstantTaskExecutorRule()
Test Repository Class (Class which have dependencies)
We gonna use test doubles for long running tasks like network requests and database queries
Test Doubles
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Fake | A test double that has a “working” implementation of the class, but it’s implemented in a way that makes it good for tests but unsuitable for production |
| Mock | A test double that tracks which of its methods were called. It then passes or fails a test depending on whether it’s methods were called correctly. |
| Stub | A test double that includes no logic and only returns what you program it to return. A StubTaskRepository could be programmed to return certain combinations of tasks from getTasks for example. |
| Dummy | A test double that is passed around but not used, such as if you just need to provide it as a parameter. If you had a DummyTaskRepository, it would just implement the TaskRepository with no code in any of the methods. |
| Spy | A test double which also keeps tracks of some additional information; for example, if you made a SpyTaskRepository, it might keep track of the number of times the addTask method was called. |
Test Coroutines
Repository testleri için coroutine kullanımı gerekiyorsa, bunun için coroutine-test kütüphanesi implemente edilmeli.
app/build.gradle altına eklenmeli
testImplementation "org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-test:$coroutinesVersion"
ve metod çağrısı runBlockingTest bloğu altında yapılmalı
fun getTasks_requestsAllTasksFromRemoteDataSource() = runBlockingTest {
// WHEN tasks are requested from the tasks repository
val tasks = tasksRepository.getTasks(true) as Result.Success
// THEN tasks are loaded from the remote data source
assertThat(tasks.data, IsEqual(remoteTasks))
}
ve metodun başına @ExperimentalCoroutinesApi annotation’ı eklenmeli.
Test UI (via Espresso)
Espresso Components
-
Static Espresso Method (e.g onView) Detail
-
ViewMatcher (e.g withId, isChekced) ViewMatcher List
-
ViewAction (e.g click) ViewAction List
-
ViewAssertion (e.g matches) ViewAssertion List
Test example - Check if checkbox’s state turn into checked on click :
onView(withId(R.id.text_username))
.perform(click())
.check(matches(isChecked()))
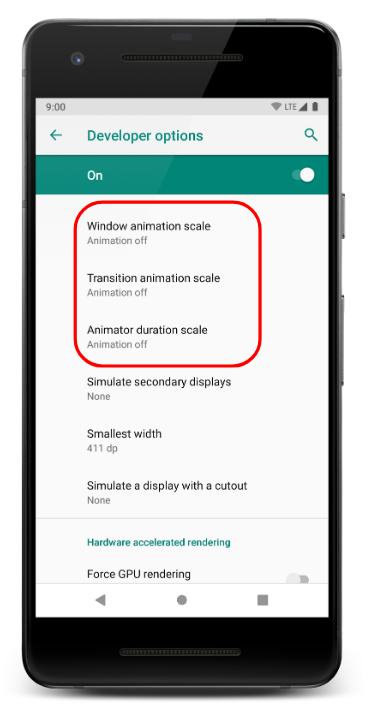
For espresso UI testing its best practice to turn off animations (From device’s developer options menu)
Test Asynchronous Code Block
-
Testing async requires determinism and synchronization mechanism
-
runBlockingTestdoes this for coroutines -
runBlockingTestusesTestCoroutineDispatcher -
gradle dependency:
kotlinx-coroutines-test
Test Room Database
-
Database test usually instrumented (Because of sqlite version differs from devices)
-
Write unit tests for DAO
-
You can use
inMemoryDatabaseBuilder()to initialize non-persistent database object for test cases -
Close database after tests
-
gradle dependency:
androidTestImplementation "androidx.arch.core:core-testing"
End-to-end Tests
Disable these three settings:
-
Window animation scale
-
Transition animation scale
-
Animator duration scale
- REFERENCES
- https://www.udacity.com/course/advanced-android-with-kotlin--ud940#